Author Affiliations
Abstract
Shanghai Jiao Tong University, State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Department of Electronic Engineering, Shanghai, China
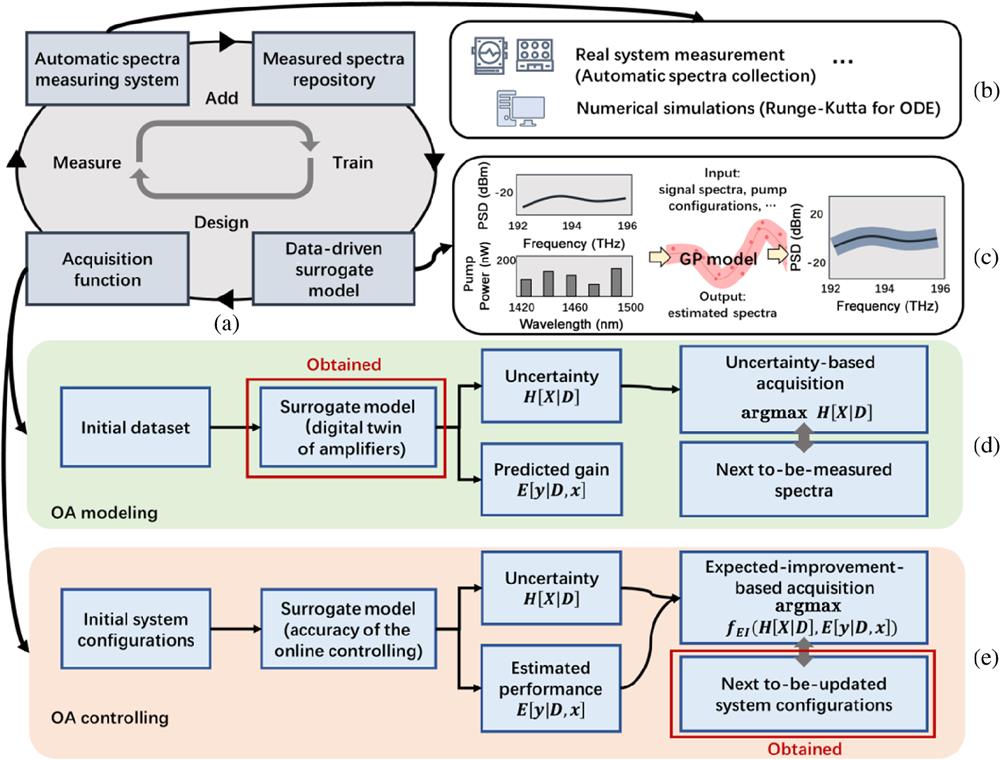
Optical networks are evolving toward ultrawide bandwidth and autonomous operation. In this scenario, it is crucial to accurately model and control optical power evolutions (OPEs) through optical amplifiers (OAs), as they directly affect the signal-to-noise ratio and fiber nonlinearities. However, a fundamental contradiction arises between the complex physical phenomena in optical transmission and the required precision in network control. Traditional theoretical methods underperform due to ideal assumptions, while data-driven approaches entail exorbitant costs associated with acquiring massive amounts of data to achieve the desired level of accuracy. In this work, we propose a Bayesian inference framework (BIF) to construct the digital twin of OAs and control OPE in a data-efficient manner. Only the informative data are collected to balance the exploration and exploitation of the data space, thus enabling efficient autonomous-driving optical networks (ADONs). Simulations and experiments demonstrate that the BIF can reduce the data size for modeling erbium-doped fiber amplifiers by 80% and Raman amplifiers by 60%. Within 30 iterations, the optimal controlling performance can be achieved to realize target signal/gain profiles in links with different types of OAs. The results show that the BIF paves the way to accurately model and control OPE for future ADONs.
optical fiber communications digital twin Bayesian inference optical amplifiers autonomous-driving optical networks Advanced Photonics
2024, 6(2): 026006
上海交通大学电子信息与电气工程学院区域光纤通信网与新型光通信系统国家重点实验室,上海 200240
飞秒激光在学术领域和工业领域都具有极高的应用价值,对飞秒激光进行准确快速的表征与精确控制对其各种应用至关重要。飞秒脉冲的传统表征方法依赖非线性效应且光路结构复杂,而飞秒脉冲的控制则大多采用开环手动调试,无法实现稳定的最优调控,极大地限制了飞秒激光的应用。近年来,智能技术的出现给飞秒激光研究提供了新范式,结合智能技术,低能量高重复频率飞秒脉冲序列的单帧全域测量与飞秒脉冲的按需智能调控有望成为现实。
锁模激光器 飞秒脉冲智能表征 飞秒脉冲智能调控 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(1): 0114006

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Shanghai Jiao Tong University, School of Electronic Information and Electrical Engineering, State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Shanghai, China
Chaotic optical communication has shown large potential as a hardware encryption method in the physical layer. As an important figure of merit, the bit rate–distance product of chaotic optical communication has been continually improved to 30 Gb/s × 340 km, but it is still far from the requirement for a deployed optical fiber communication system, which is beyond 100 Gb/s × 1000 km. A chaotic carrier can be considered as an analog signal and suffers from fiber channel impairments, limiting the transmission distance of high-speed chaotic optical communications. To break the limit, we propose and experimentally demonstrate a pilot-based digital signal processing scheme for coherent chaotic optical communication combined with deep-learning-based chaotic synchronization. Both transmission impairment recovery and chaotic synchronization are realized in the digital domain. The frequency offset of the lasers is accurately estimated and compensated by determining the location of the pilot tone in the frequency domain, and the equalization and phase noise compensation are jointly performed by the least mean square algorithm through the time domain pilot symbols. Using the proposed method, 100 Gb / s chaotically encrypted quadrature phase-shift keying (QPSK) signal over 800 km single-mode fiber (SMF) transmission is experimentally demonstrated. In order to enhance security, 40 Gb / s real-time chaotically encrypted QPSK signal over 800 km SMF transmission is realized by inserting pilot symbols and tone in a field-programmable gate array. This method provides a feasible approach to promote the practical application of chaotic optical communications and guarantees the high security of chaotic encryption.
chaotic optical communication physical layer security deep learning digital signal processing Advanced Photonics Nexus
2024, 3(1): 016003
1 上海交通大学电子信息与电气工程学院区域光纤通信网与新型光通信系统国家重点实验室,上海 200240
2 杭州爱鸥光学科技有限公司,上海 200240
高功率窄线宽连续光纤激光器在科学研究、工业加工和**功防领域具有广泛的应用价值。在保证激光器输出质量的前提下,不断提升输出功率是高功率激光器不懈追求的关键目标之一。受激布里渊散射效应是制约激光功率提升的关键因素之一,本文针对受激布里渊散射效应展开,重点介绍基于光谱展宽的非线性效应抑制方法的不同方案与效果,综述利用相位调制展宽种子源光谱的发展历程,分析当前存在的问题并展望该技术的发展前景。
激光器 高功率窄线宽连续光纤激光器 光谱展宽 相位调制 受激布里渊散射效应 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(15): 1500001
1 宁波大学高等技术研究院红外材料及器件实验室, 浙江 宁波 315211
2 上海交通大学区域光纤通信网与新型光通信系统国家重点实验室, 上海 200240
硫系玻璃具有较宽的红外透过范围及极高的线性和非线性折射率。综述了基于受激布里渊散射效应的硫系玻璃光器件研究进展,以及硫系光纤和波导器件在布里渊激光器、慢光产生和微波光子滤波器等领域的应用现状,指出了研究中存在的问题,并展望了其发展前景。
非线性光学 受激布里渊散射效应 硫系玻璃光纤和波导 受激布里渊散射阈值 激光与光电子学进展
2019, 56(3): 030001

Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
We propose a general guideline on the design of a stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS)-based microwave photonic filter (MPF) using a directly modulated pump. Filter gain profiles and passband ripples with waveform repetition periods of the driving current ranging from 2 to 100 ns are measured after the transmission of different fiber lengths. The results show that the filter performance has nothing to do with the fiber length, and the digital-to-analog converter bandwidth requirement for the driving current is no more than 500 MHz. Therefore, the low cost, flexible reconfiguration, and miniaturization characteristics make an SBS filter using a directly modulated pump a promising choice as an MPF.
060.5625 Radio frequency photonics 290.5900 Scattering, stimulated Brillouin 060.2330 Fiber optics communications 060.4080 Modulation Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(6): 060603
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
We extensively discuss 25 Gb/s per wavelength capacity in both IEEE and ITU-T standardization to support the increasing bandwidth requirement. In this Letter, we propose to use the optical dispersion compensation technique in an optical line terminal (OLT) combined with a bandwidth-limited electro-absorption modulated laser in an optical network unit to achieve 25 Gb/s capacity for the upstream link. We evaluate the positive and negative dispersion tolerances of 25 Gb/s electrical duo-binary (EDB) and pulse-amplitude modulation (PAM-4) signals. We achieve 39.5 and 31 dB upstream loss budgets for the 25 Gb/s EDB and PAM-4 signals by using 600 and 500 ps/nm optical dispersion compensation in OLT, respectively, both supporting 0–40 km differential reach.
250.4110 Modulators 230.0040 Detectors Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(2): 022502
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Wuhan National Lab for Optoelectronics (WNLO) & National Engineering Laboratory for Next Generation Internet Access System, School of Optical and Electronic Information, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430074, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Network, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240, China
3 State Key Laboratory of Optical fiber and Cable Manufacture Technology, Yangtze Optical fiber and Cable Joint Stock Limited Company (YOFC), Wuhan, 430073, China
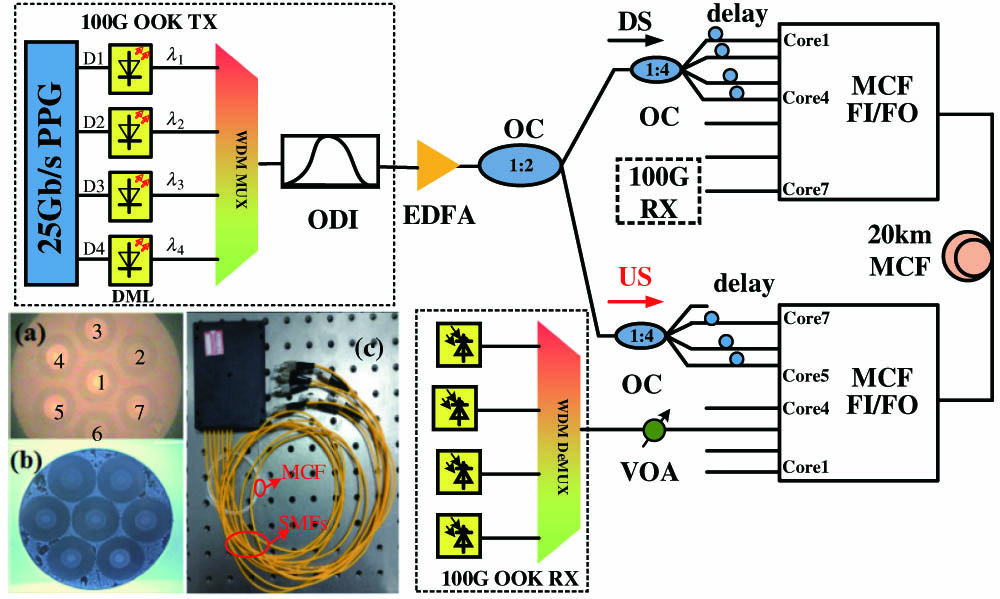
We experimentally demonstrate a real-time quasi-full-duplex 400G/300G optical interconnection over 20 km multicore fibers (MCFs), using 10G-class transponders operated in the C-band. Optical delay interferometer (ODI)-based optical frequency equalization is applied to mitigate chirp and dispersion induced impairments, so that the tolerance to inter-symbol interference (ISI) can be enhanced, thus enabling 4×25 Gb/s on-off keying (OOK) transmission per core over severely limited bandwidth channels. Real-time bit error ratio (BER) performances of the bidirectional 400 Gb/s transmission are measured without using extra digital signal processing (DSP) or electrical equalization, which ensures low complexity and less power consumption.
060.0060 Fiber optics and optical communications 060.4510 Optical communications Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(8): 080602
The State Key Lab of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Department of Electronic Engineering,Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
In this paper, the key technologies and research progress of chaotic optical communication are reviewed. We first discuss the chaos generation methods based on different nonlinear components. Then we focus on the frontiers of chaotic optical communications, including how to improve the security, and the development about the transmission capacity and distance of chaotic optical communication in laboratory and field. At last, we discuss limitations and potentials of chaotic optical communications and draw a conclusion.
chaos chaos chaotic optical communications chaotic optical communications security security capacity capacity time delay concealment time delay concealment Frontiers of Optoelectronics
2016, 9(3): 508
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 The State Key Lab of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Shanghai Jiao Tong University,Shanghai 200240, China
2 Department of Physics, Southeast University, Nanjing, China
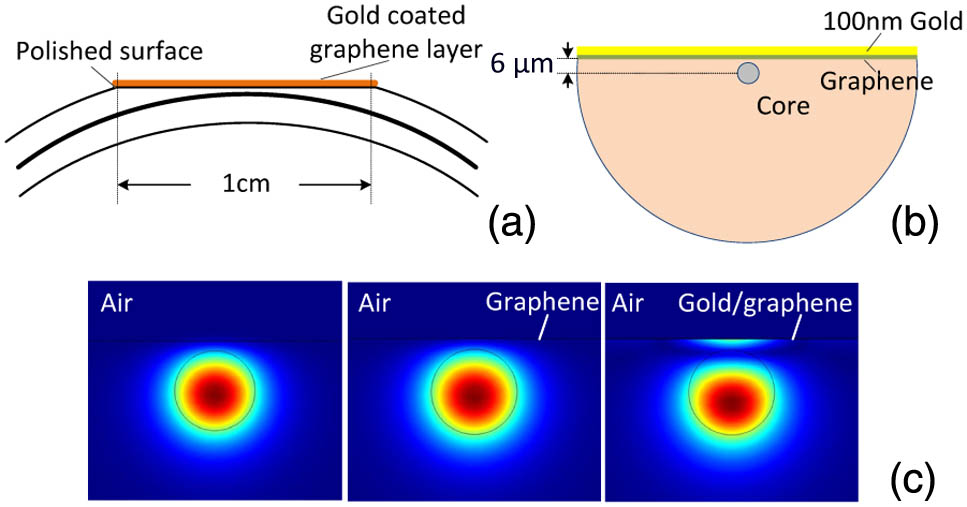
By transferring 100 nm gold-coated CVD monolayer graphene onto the well-polished surface of D-shaped fiber, we achieve a graphene in-line polarizer with a high polarization extinction ratio of ~27 dB and low insertion loss of 5 dB at 1550 nm, meanwhile achieving a strong saturable absorption effect of 14%. The manufacture of thisgraphene in-line polarizer also simplifies the graphene transfer process. To explore the potential applications of the new device, we also demonstrate noise-like pulse generation and supercontinuum spectrum generation. By launching the designed graphene device into a fiber ring laser cavity, 51 nm bandwidth noise-like pulse is obtained. Then, launching the high-power noise-like pulse into high nonlinear fiber, a 1000 nm wide supercontinuum spectrum is obtained, which is favorable for sensing and nonlinearities scientific fields.
Lasers Lasers fiber fiber Mode-locked lasers Mode-locked lasers Photonics Research
2016, 4(2): 02000041





